Applied Artificial Intelligence: How AI Transforms 5 Industries
 This article was written by the I Know First Research Team.
This article was written by the I Know First Research Team.In late 18th century, the British textile industry spearheaded a process that would become known as the First Industrial Revolution, which saw first factories appear and new manufacturing processes introduced. Then, the Second Industrial Revolution followed on the back of railroads and telegraphs enabling quick movement of people and ideas and Henry Ford’s moving assembly line beefing up the industrial output to new heights. The Third Industrial Revolution saw manufacturing go digital, with computers brought in to run and streamline the process, and now, some are speaking of a Fourth Revolution – one driven by applied artificial intelligence.
While that may or may not be an overstatement, a fact is a fact: the AI industry is booming. And as it rises to new heights, artificial intelligence is applied across a growing number businesses, doing all sorts of things that used to be purely human endeavors. Furthermore, the technology is transforming whole industries, making businesses find new sophisticated ways to maintain and develop the customer bases, conduct their R&D and trial runs and operate their manufacturing.
And if you want to keep pace with the world as the era of AI ushers upon it, here is an overview of how applied artificial intelligence will transform 5 key industries.
AI In Marketing: Know Thy Customer
Given the trouble that online giants like Facebook and Apple have recently found themselves in and the ongoing public discussion over privacy and personal data, it would be unfair to start our overview with anything but AI in marketing.
The first thing to note here is that humans, if given all the social media that are out there these days, will generate a gargantuan flow of data, not excluding the way they feel about different products and ad campaigns. This data could be processed to get a better understanding of their preferences as customers and their needs. While this could be problematic for a human operator, deep learning-based (add link to article on deep learning) AIs are naturally good at deriving meaningful insights from huge streams of unstructured (i.e. not specifically structured in a way that would be easy for a machine to digest) data. This makes them a perfect fit with the marketing crowd, which is eager to reap the boons of the new era.
That is why it is not a surprise that we are living through a real boom of AI-driven marketing these days. In fact, some of its manifestations are so humongous in scale that they seem downright dystopian. Let us take the aforementioned Facebook, for example – some reports suggest that the company’s proprietary AI has got so advanced that it can not just track people’s customer preferences to tailor the ads they see, but even gauge their customer loyalty. What this means is that the machine tries to predict when a customer of company A could decide to go for products from company B, allowing company A to bombard its client with tailored ads and prevent a shift of loyalty.
While this was an extreme example, there are troves of other apps and services that provide for high-tech marketing without Orwellian undertones. For example, Netflix, the streaming giant, utilizes AI in content curation, using an advanced model to make sure that the show and movie suggestions are individually tailored to the tastes of each subscriber. Natural Language Processing services like Phrasee help automate ad text generation. Web design, an important part of building up your image, can also be automated by using AI-driven services like the Wix ADI or Jimdo Dolphin. A huge variety of services is available for those who want to make their analytics smarter, including all-around solutions like albert.ai, or services like Nudge, that are focused on helping you build relations with your customers. Sensai is there to help you with social media management, Botsify will help you create bots eager to chat with your customers… The opportunities are endless.
AI In Manufacturing: How To Train Your Factory
The references to the Industrial Revolution in the introduction of the article did not come out of the blue. Given that computers are omnipresent these days, manufacturing involves a lot of smart tech, which, once again, generates troves of data as it goes through thousands of production cycles. Thus, it is hardly a surprise that the mighty AI tech has already entered the manufacturing industry, and its applications are as diverse as they are efficient.
Let us start with the obvious – with machine learning algorithms implemented in the very robots that do a lot of the dirty work these days. Some of them now feature machine vision capabilities, a deep learning-based process that allows the machine to process visual data and learn from it. When imbued with this power, industrial robots can optimize the ways to manufacture sophisticated components, change the course of action on the go in case of a mistake and perform quality-control. Companies like Aquifi and LMI Technologies have already made this a reality, giving industrial robots the special awareness they never really had before.
Furthermore, with all the data generated by smart factories in real-time, the door is open to apply another major Ai capability – data-driven prediction. An industrial AI can go over the whole manufacturing pipeline to identify bottlenecks, it can also keep track of its operations, trying to predict the next point where any sort of trouble might happen. This has already been implemented by LG, allowing to prevent thousands and thousands dollar worth of losses.
The starting and end-points of manufacturing can also benefit from implementation of AI-driven solution. Powerful AI-based generative design tools are used to assist engineers in designing the geometry of the components, greatly reducing the amount of time that is spent on this aspect. This approach has already been utilized by General Motors and Airbus. Machine vision also enables AI to play a role in packaging and distribution, transforming a modern warehouse into a smart distribution hub filled to the brim with AI-driven robots.
AI In Healthcare: Ki… Heal All Humans!
In mass culture, one of the most common tropes is an AI rebelling against it creators and waging a bloody conquest upon the war-torn Earth. Should this ever happen, it would be pretty ironic to see robo-doctors tending the wounds of the human soldiers as they fight off the hordes of murderous machines.
Jokes aside, tough, healthcare and medicine are another major area that could benefit from the rise of AIs and advanced machine learning. As always, when it comes to the AIs in their current shape and form, it all comes down to data. A patient’s medical record provides a whole variety of data points, which, if studied in tandem with records of discussions with the doctors, search history and various other sources of information represent a trove of data for the machine to munch on. Add similar data on other patients, and you get a huge dataset that, if coupled with a deep learning algorithm, will produce an AI capable of diagnosing and monitoring the patients.
This kind of logic lies at the foundation of successful projects like an AI that uses clinical data to identify pediatric diseases, for example. Another AI, one that relied on machine vision for processing MRIs of human brains, successfully defeated human doctors in a competition where they were supposed to identify and predict the development of brain tumors. Chatbot developed by UK-based Babylon Health company also tries to diagnose the patient, but this time, through asking them a series of questions.
The application of AI in healthcare does not end with diagnosis. Machine vision enables AI-driven robo-surgeons to assist their human counterparts. AIs can also be utilized in other areas that require a through data analysis, such as pathology. Furthermore, projects like IBM Watson Health, which puts the power of the company’s supercomputer at the service of healthcare professionals, seek to bolster oncological research and help doctors take on Alzheimer’s. It also strides into pharmaceuticals, aiming to help companies identify new drugs quicker. And while the project has seen its downs, AIs seem set to have a major impact on healthcare of tomorrow.
AI In Energy: Green & Smart Go Hand-In-Hand
Climate change is a major issue for the public this days, as indicated both by the massive international youth activism calling for climate action and the strong performance of the Green parties in the EU Parliament elections. This means that green tech is going to play an increasingly important role in the future, regardless of whether you would prefer to see it as an answer to the popular demand or the lifeline of a planet in danger. And since the energy sector is one of the traditional sources of pollution, the push for renewables can be expected to grown more and more powerful every year.
AI could have a role to play here, and here is how that could work out. Renewables, whether it comes to solar power, wind or anything else, do lag behind oil and coal in terms of pure energy efficiency. In other words, a whole batch of solar batteries cannot deliver power at the same speed, volume and price as a conventional power plant can. No AI can fix that, of course; what an AI can do, however, is run the smart grid that would cover this gap through making energy supplies as efficient as possible. Monitoring and predicting the trends in energy consumption based on historical data and inputs like weather forecasts, it would make sure that every watt of power is delivered at the right place at the right time. This may not necessarily make green power feasible and sustainable everywhere, but it is easy to see why a system like that would be a gift to conventional power suppliers as well. And that’s not to mention the consumers, who could benefit from access to smart meters, which would allow them to plan their energy consumption in line with the dynamically changing prices.
The technology for all this is already there, but we are yet to see a truly smart, AI-driven grid. There are still, however, successful examples of AI being used in the renewable energy sector. Projects like VADER and Nnergix aim to increase the efficiency of renewables-based power grids through addressing their vulnerability to weather conditions. They model the power consumption patterns, while also looking at the data from the sensors to assess the weather in the area.
AI is also utilized in power storage, once again, assessing the patterns of energy consumption and generating savings for both consumers and suppliers. Stem’s Athena service, one of the oldest in this sphere, is a good example. Processing data at the speed of 400 Mb per minute, it optimizes the power output within the grid in line with the timing of peak consumption periods. SparkCognition, in its turn, demonstrates that there’s more to AIs in energy than just smart grid: it utilizes AI to make coal plants safer through predicting infrastructure failures.
AI In Finance: Making Money Go Smart
We live in a time when everything goes smart, from mobile phones to cars and houses. In this era, it would be quite appropriate for money to go smart as well – and the financial sector is keeping up with the trend, implementing all sorts of AI-based solutions.
Here, artificial intelligence is applied with a whole variety of goals in mind. For example, the classical machine learning task of classification, when introduced to the exciting world of transactions, helps businesses filter out credit card fraud. The AI looks at the transaction, checks it against the customer’s history and tries to figure out whether there is something fishy going on. That is the idea behind such services as Riskified, which seeks to protect its customers from such misfortunes. In a similar fashion, banks look at the profiles of those applying for loans in order to estimate the probability of default; that is also classification in action. AIs like Auger deal with such risks, going through the applicants’ data in a search for troubling signs.
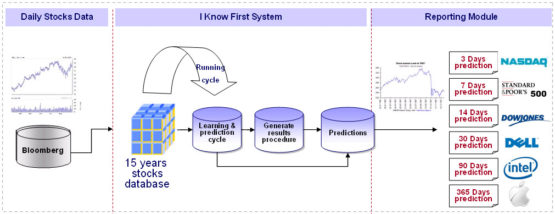
Even more exciting, however, is the prospect of using AI to predict the dynamics of stock markets in hopes of big returns for investors. Here, AI is fueling the rise of the new brand of quantitative hedge funds, those relying on advanced algorithms to try to forecast what happens on the markets tomorrow. And if the idea of Algo-trading does look intriguing to you, we can point at I Know First, an Israel-based daily market forecast company that has developed a proprietary AI to stay one step ahead of the trading.
The algorithm has been built with elements of chaos theory, deep learning and genetic programming incorporated in its design. Trained on a database covering 15 years of trading, it is fed fresh market data every day; scouring it for trends and patterns, it reconfigures its existing models to be better attuned to the reality at hand. It also learns from its prior successes and failures, increasing the accuracy of its predictions with every iteration.
The algorithm is familiar with over 10,000 financial instruments, including stocks, ETFs, currencies and commodities. Its predictions cover a variety of time horizons, ranging from 3 to 365 days and thus incorporating short, medium and long-term prospects. Its output is delivered as a heatmap, with numeric indicators for signal and predictability. Signal is indicative of how the stock is expected to perform in comparison to other assets on the forecast: high positive values mean the algorithm expects the stock to go up, while big negatives mean a nosedive could be expected. The predictability score, in its turn, demonstrates how well the algorithm has performed in predicting the stock’s dynamics in its previous forecasts.